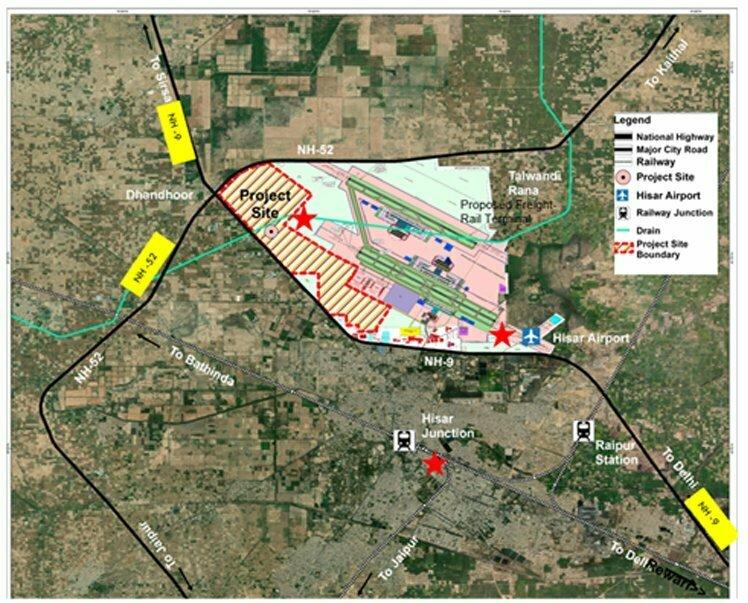
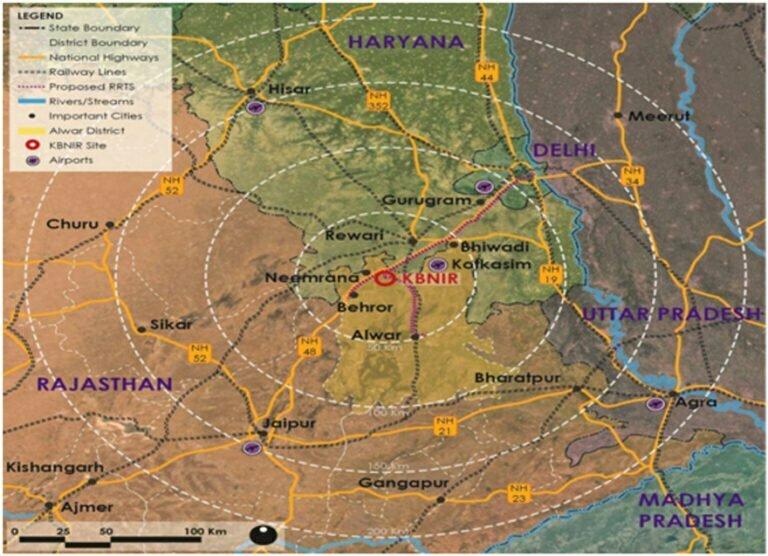
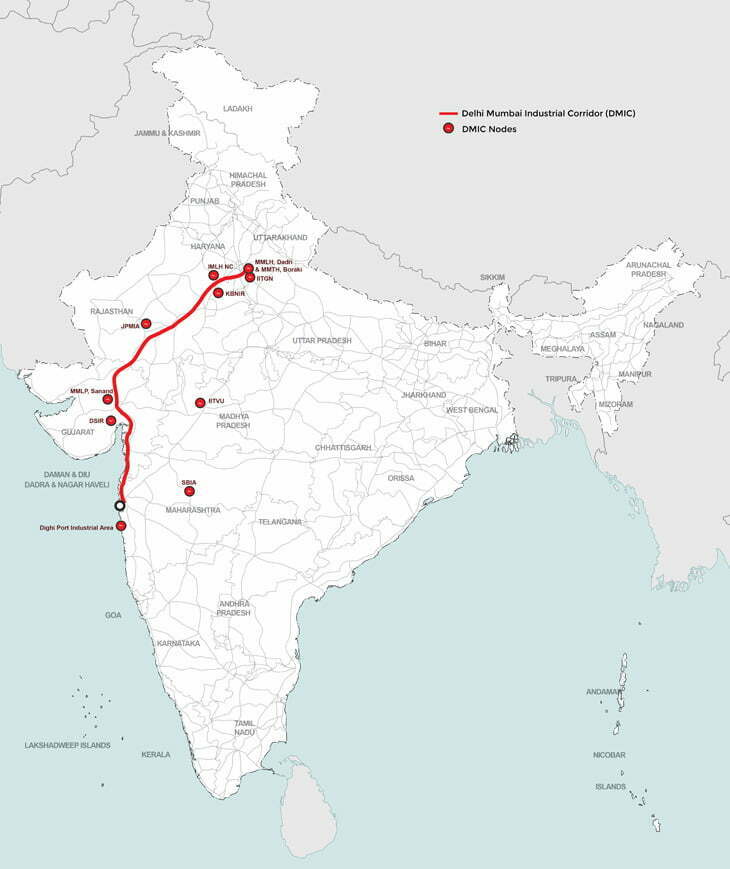
The Union Cabinet, led by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, recently sanctioned the development of 12 industrial smart cities across 10 states, under the National Industrial Corridor Development Programme (NICDP). These projects, aimed at transforming India’s industrial landscape, involve an estimated investment of Rs 28,602 crore. With the strategic intent of enhancing domestic manufacturing, attracting foreign investments, and creating jobs, these cities are expected to boost the country’s global competitiveness and economic growth.
Key Objectives of the Smart Cities Initiative
- Investment Attraction: The government projects a potential investment of Rs 1.52 trillion from both large anchor industries and MSMEs (Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises).
- Job Creation: The initiative is expected to generate 1 million direct jobs and an additional 3 million indirect jobs, providing economic upliftment to regions where the cities are located.
- Focus on Sustainability: A core focus is on sustainability, with the cities incorporating green technologies and ICT-enabled infrastructure to minimize their environmental footprint.
- Global Value Chains (GVCs): The program positions India to play a pivotal role in global value chains, encouraging the establishment of manufacturing hubs across the country.
Locations and Development Plan
The 12 industrial smart cities will be spread across 10 states, ensuring balanced regional development. These are some of the key locations:
- Khurpia in Uttarakhand
- Rajpura-Patiala in Punjab
- Dighi in Maharashtra
- Palakkad in Kerala
- Agra and Prayagraj in Uttar Pradesh
- Gaya in Bihar
- Zaheerabad in Telangana
- Orvakal and Kopparthy in Andhra Pradesh
- Jodhpur-Pali in Rajasthan
Notably, one city’s name has been withheld due to the Model Code of Conduct in place for poll-bound states.
Infrastructure and Development Focus
The cities will adopt greenfield development models, built “ahead of demand” with an emphasis on “plug-and-play” and “walk-to-work” concepts. These models ensure that industrial setups have access to ready-to-use infrastructure, reducing setup times for manufacturing units.
The government is also placing strong emphasis on multi-modal connectivity through the PM GatiShakti National Master Plan, which will ensure seamless transportation and movement of goods, services, and people. This integration of logistics with manufacturing infrastructure will improve supply chains and boost efficiency across the sectors.
Targeted Industries and Future Growth
These industrial hubs will focus on a variety of industries, such as:
- Electric vehicles
- Technical textiles
- Aero logistics
- Fabrication
- Food processing
- Tourism
For example, Hyundai has already committed to setting up an automobile hub on 450 acres at the Zaheerabad smart city in Telangana, even before the official approval of the project. This demonstrates the strong potential of the initiative to attract large-scale foreign investment.
These cities are expected to play a crucial role in helping India achieve its ambitious goal of $2 trillion in exports by 2030.
Government Collaboration and Global Partnerships
The development of these industrial smart cities is a joint effort between the Union and State governments. While states contribute land, the central government offers equity or debt, depending on the project. Additionally, partnerships with countries like Switzerland and Singapore are being explored to bring in international expertise for industrial town planning.
NICDP and Competitor Comparison
The NICDP’s industrial cities are designed to surpass traditional industrial setups by offering superior, integrated infrastructure. Here’s a comparison of the NICDP cities with other existing industrial setups:
| Feature | NICDP Smart Cities | Traditional Industrial Parks | SEZs (Special Economic Zones) | Private Industrial Cities |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Investment Size | Rs 28,602 crore | Smaller, region-specific | Varied based on state policies | Investor-driven |
| Job Creation | 4 million (direct & indirect) | Lower due to smaller scale | Higher for export-driven industries | Dependent on projects |
| Sustainability Focus | High (Green tech, ICT) | Medium | Varies by project | High |
| Multi-modal Connectivity | Integrated with GatiShakti Plan | Limited to state-level infrastructure | Dependent on location | High (Private investments) |
| Foreign Investment | Actively encouraged | Limited | Encouraged through specific schemes | Primarily private |
The NICDP smart cities are clearly positioned to offer competitive advantages, including sustainability, job creation, and foreign investment attraction, making them stand out from other industrial initiatives.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the main purpose of developing these industrial smart cities?
The main purpose is to attract foreign and domestic investment, boost industrial production, and create job opportunities while ensuring sustainable development.
2. How do these cities differ from traditional industrial zones?
These smart cities are designed with advanced infrastructure, focusing on sustainability and seamless connectivity, whereas traditional zones may not have such integrated, futuristic planning.
3. Which industries will benefit the most from these projects?
Industries such as electric vehicles, technical textiles, aero logistics, and food processing will significantly benefit due to the advanced infrastructure tailored to their needs.
4. How will this project impact India’s export goals?
By creating a network of globally competitive industrial hubs, the project aims to help India achieve $2 trillion in exports by 2030.
5. Are there any international collaborations in this initiative?
Yes, countries like Switzerland and Singapore have expressed interest in partnering with India to develop these industrial cities.
Conclusion
The development of 12 industrial smart cities under the NICDP marks a significant milestone in India’s journey toward becoming a global manufacturing hub. With its focus on sustainability, job creation, and strategic infrastructure, this initiative will transform India’s industrial landscape, attract foreign investments, and boost economic growth in the coming years. These cities represent a futuristic approach to industrialization, blending economic growth with environmental stewardship, and are expected to play a crucial role in achieving India’s Viksit Bharat vision of a developed India.