India’s Industrial Growth and the Role of Special Investment Regions
India has witnessed remarkable economic growth over the past decade, with a nearly 6% annual GDP growth rate, making it one of the world’s leading economies. A pivotal factor in this success is industrial development, a focus area for the Indian government as it aims to ensure a resilient and prosperous future.
The Vision for a Resilient India
As India celebrates 75 years of independence, the government is committed to creating a vision for a sustainable future, focusing on:
- Employment Opportunities: Creating value-added jobs for a better livelihood.
- Improved Quality of Life: Developing affordable housing and sustainable communities.
- Environmental Goals: Prioritizing green initiatives to ensure eco-friendly development.
- Enhanced Connectivity: Facilitating efficient movement of goods, services, and people.
These goals form the foundation for a sustainable India, driven by industrial growth and supported by a young population, rising income levels, and governance focused on inclusive growth.
India’s Path to Global Economic Leadership
Despite the challenges of the recent pandemic, India is on track to become the world’s third-largest economy by 2030. However, rapid economic growth often brings challenges like unplanned urbanization. To achieve balanced development, equitable economic growth across different regions is essential. Strategic initiatives, such as the creation of economic nodes in underdeveloped regions, help distribute growth more evenly and reduce migration pressures on major cities.
Challenges of Urbanization in India
Urban India today accounts for around 55-60% of the country’s GDP, with mega cities facing intense population pressures due to migration. This surge strains infrastructure, posing challenges in providing basic amenities like water, electricity, and public safety. To address this, India needs policies promoting equitable growth across both major and smaller cities, enabling economic stability across regions.
Developing Industrial Corridors for Balanced Growth
A core strategy to foster equitable economic benefits is the development of industrial corridors led by the National Industrial Corridor Development Corporation (NICDC). These corridors are designed to:
- Utilize multimodal transport networks like railways and highways.
- Establish economic nodes across various regions, encouraging sustainable urbanization.
- Reduce migration to mega cities by generating local employment opportunities.
Expanding Industrial Corridors Across India
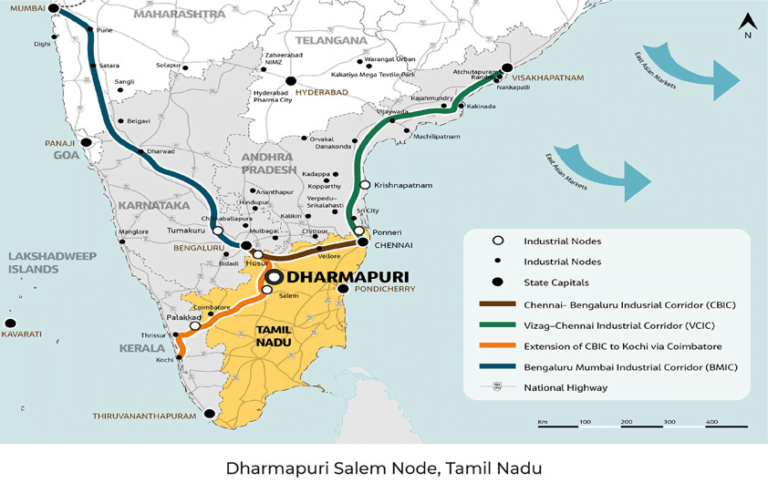
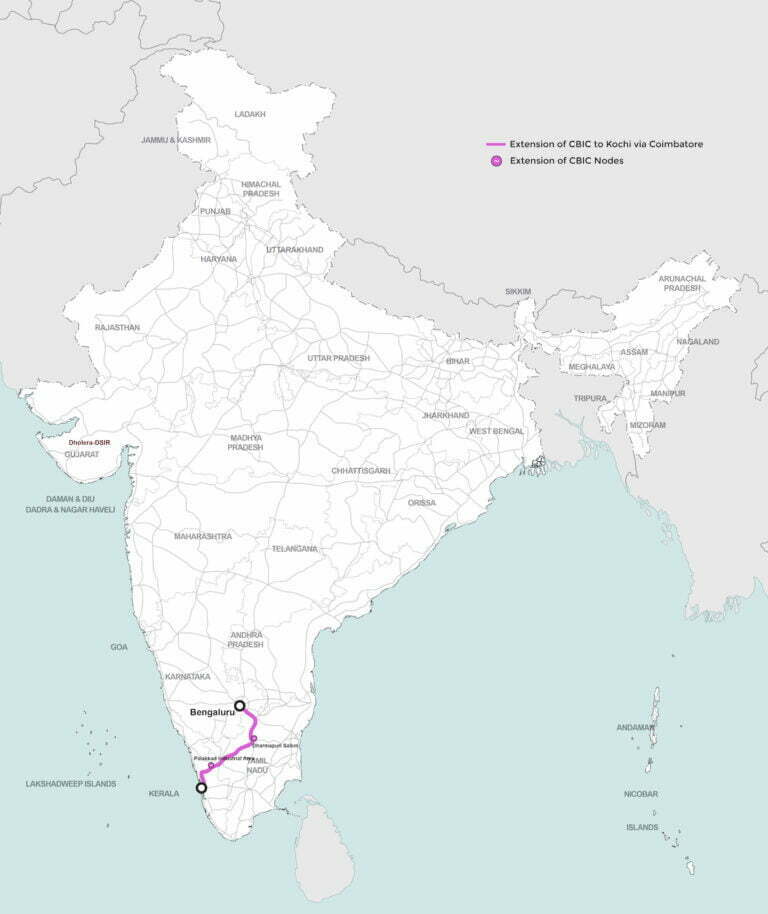
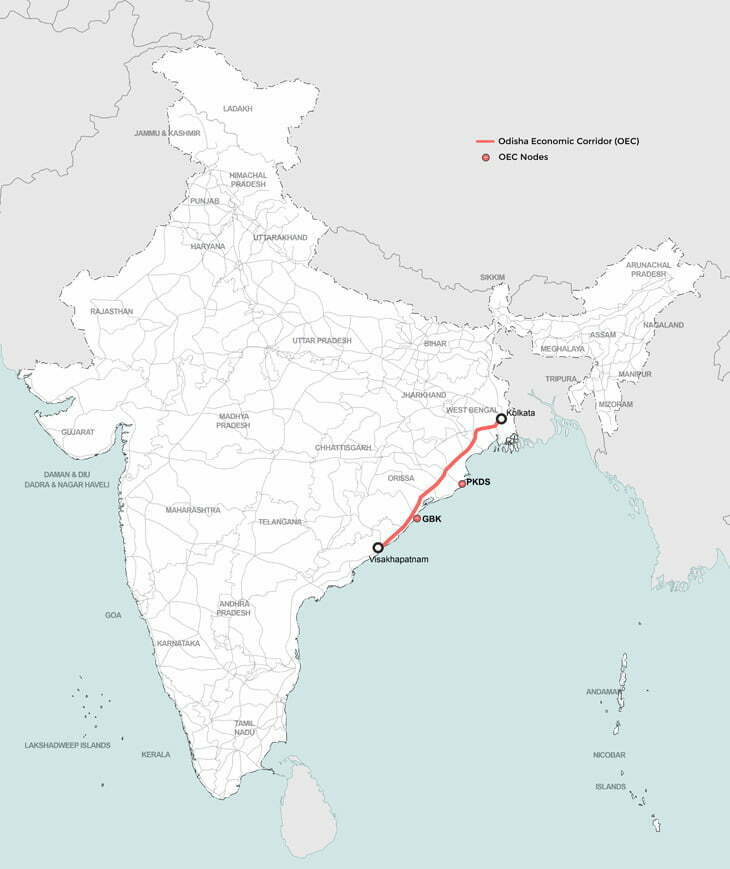
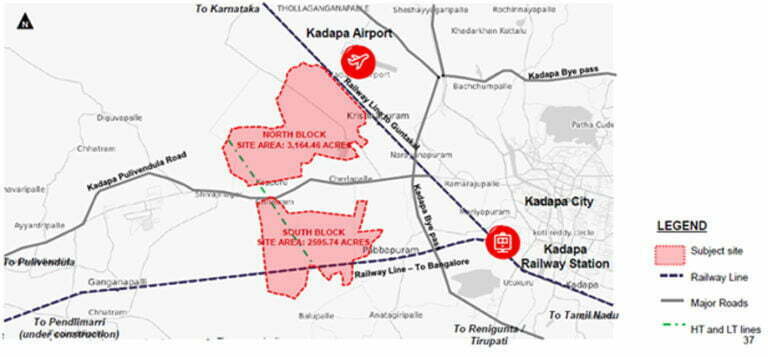
Under the government’s ambitious vision, the NICDC is implementing 11 industrial corridor projects nationwide, expanding beyond the initial Delhi-Mumbai corridor. These corridors aim to bring economic opportunities to remote areas, fostering balanced growth. Each corridor is planned as a self-sustaining ecosystem, incorporating residential, commercial, healthcare, and entertainment facilities to promote a “walk-to-work” lifestyle.
Dholera Special Investment Region: A Model for Integrated Development
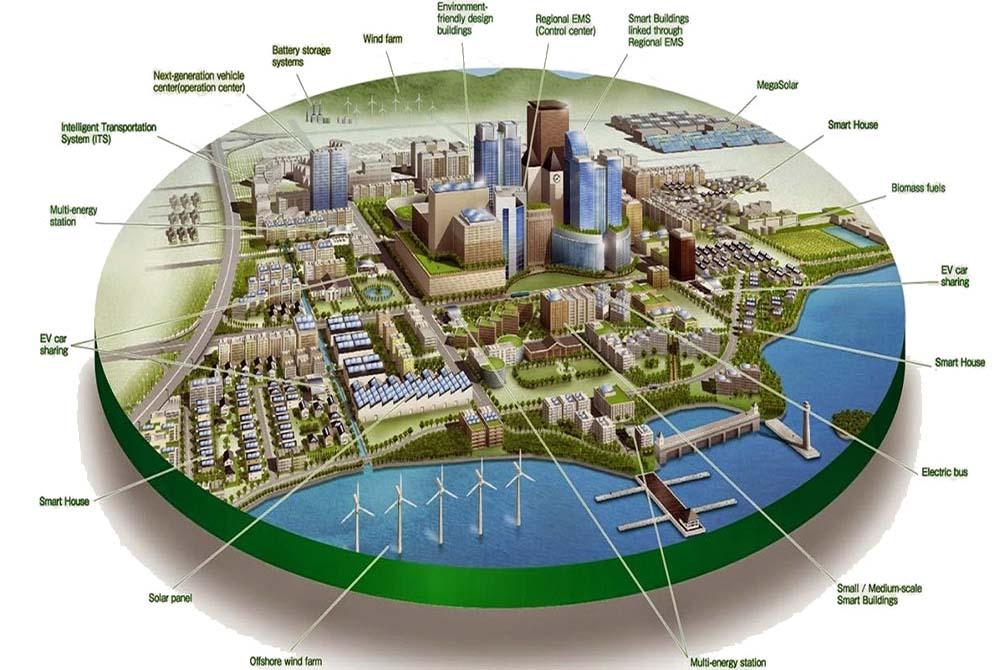
The Dholera Special Investment Region (DSIR) is a leading example of this approach, combining industrial infrastructure with quality social and residential amenities. Affordable housing, a cornerstone of the government’s policy, is prioritized here, reflecting the goal of providing housing for all. The DSIR exemplifies how industrial corridors can drive job creation while meeting the housing needs of all income levels.
Historical Precedents and Future Outlook
India’s history of industrial towns, like Jamshedpur and Bhilai, demonstrates the impact of industrialization on urbanization. However, these towns have often struggled with unplanned growth. The NICDC’s current corridor projects draw on these lessons, introducing sustainable practices for long-term success. Through careful planning and innovative approaches, the NICDC aims to address challenges in urban sustainability and community resilience.
The Role of the National Industrial Corridor Development Programme
The National Industrial Corridor Development Programme emphasizes proactive planning of infrastructure before industrial development begins. Key aspects of this program include:
- Creating robust urban infrastructure such as transport, connectivity, and utilities.
- Ensuring infrastructure development is in place before industrial growth, enabling seamless urban expansion.
- Supporting smaller towns and cities through investment in transportation and last-mile connectivity.
The government’s Gati Shakti Master Plan plays a vital role in these efforts, aiming to connect major industrial clusters to smaller economic towns and promoting seamless logistical linkages.
Employment and Economic Impact
It is estimated that each acre of industrial development can generate around 50-60 jobs. This growth not only stimulates demand for housing but also bolsters the service sector, creating jobs in banking, logistics, and hospitality. Industrial corridors thus have the potential to elevate regional economies, fostering both residential and commercial development.
Sustainability and Climate Resilience in Industrial Nodes
Sustainability and climate resilience are central to the development of new industrial townships. Measures such as renewable energy usage, rainwater harvesting, and eco-industrial parks underscore the commitment to long-term sustainability. The NICDC’s focus on green infrastructure ensures these regions remain habitable and environmentally friendly.
Private Sector Involvement and Future Initiatives
Encouraging private sector participation is essential for the success of these industrial nodes. The government is fostering this by offering incentives such as access to financing and land, along with attractive concession agreements. Integrated townships appeal to private developers as they offer revenue from higher rent-yielding assets, making industrial corridors an appealing investment opportunity.
Integration with Government Schemes
One of the NICDC’s most notable achievements is its integration of various government schemes under a unified approach. Initiatives such as housing for all, rental housing schemes, and urban rejuvenation are embedded within the industrial corridor projects. This comprehensive strategy drives both economic and social development, setting the stage for India’s future growth.